Image by PublicDomainPictures from Pixabay
What is Bagasse?
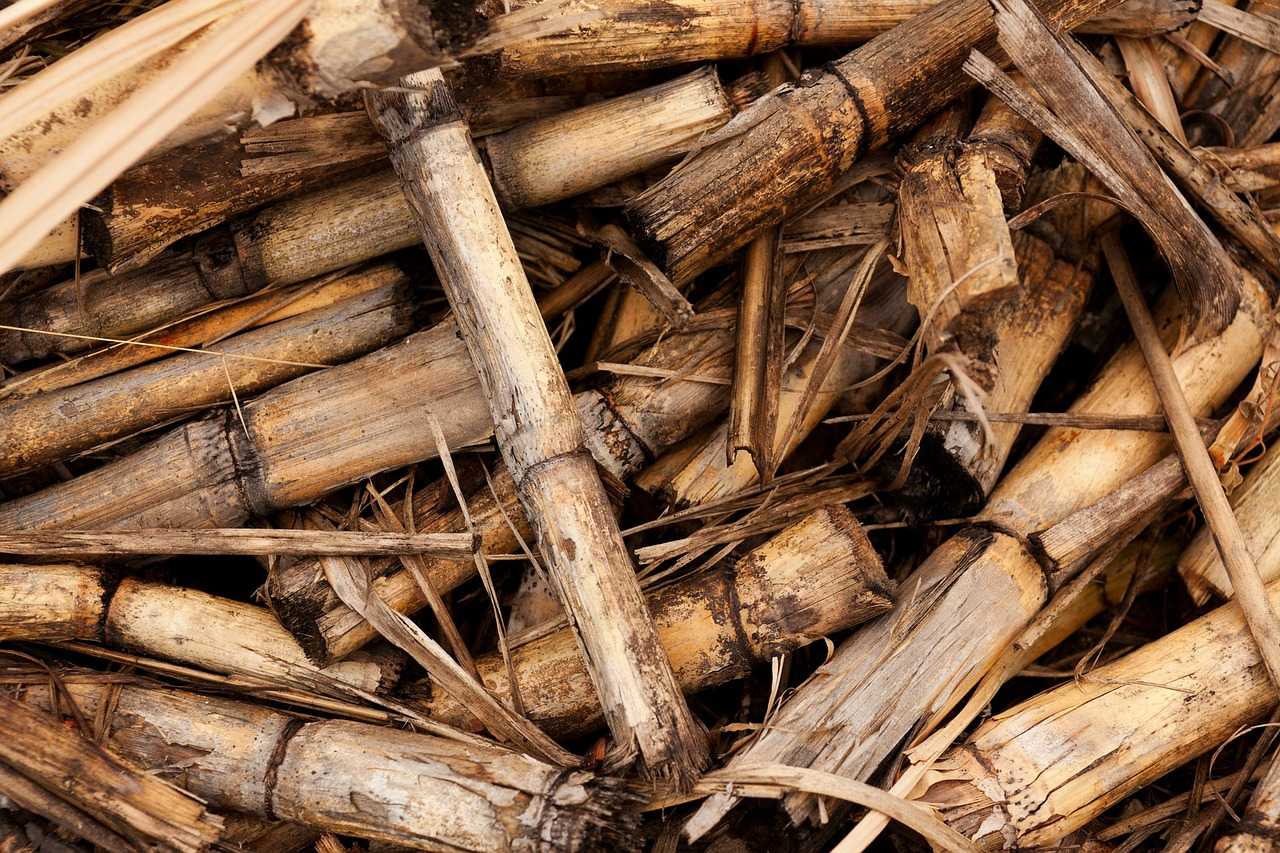
Bagasse is a fiber that remains after the extraction of the sugar-bearing juice from sugarcane. It is also known as megass and megasse. The word bagasse, from the Spanish bagazo, originally meant “refuse,” “rubbish,” or “trash.”
Applied first to the debris from the pressing of grapes, palm nuts, and olives, the word was eventually used to mean leftovers from other processed plant materials, such as sugar beets, sugarcane, and sisal. Today, however, the word is used just for the by-product of the sugarcane mill.
It consists of 40 – 60% cellulose, 20 – 30% hemicellulose, and about 20% lignin. It’s one of the most promising lignocellulosic but generally underutilized materials.
In the past, it was mainly seen as a waste product and used as a fuel in co-generation power plant to generate power or burned as fuel in the sugarcane mill. Its value highly increased since recycling became a usual part of every production process and modern society, in general.
A number of researches have explored using bagasse for the production of bio-based materials and as a renewable power generation source. Some of the most common uses of bagasse are for pulp, feed, board, paper, and fuel.
Top countries in sugarcane production (and logically, it’s residue, bagasse ) are located in Latin America and Asia – Brazil, India, China, Thailand, Mexico, and Colombia. Also, there is Argentina which contributes to 1,1 % of world sugarcane production.
Cuba has a great potential in sugarcane production, and energy derived from bagasse is currently under review.
Bagasse as a “Green” Power Source
It is usually used as the main fuel source for sugar mills. Bagasse produces heat energy to supply all the needs of a typical sugar mill, when it is burned in quantity, with energy to spare.
Furthermore, the second use for this waste product is in cogeneration. This use provides both – heat energy and electricity.
The first is used in the mill, and the second is typically sold on to the consumer electricity grid. The CO2 emissions are less than the amount that the sugarcane plants absorb from the atmosphere during its growing phase. For this reason, it makes the process of cogeneration greenhouse gas-neutral. In a number of countries, sugar factories significantly contribute ‘green’ power to the supply of electricity.
“Thankfully” to the increased pollution and climate changes, caused by power production, the world is now looking for renewable sources of energy. The mills in Brazil generate on average 12kWh of electricity per ton of bagasse, 330 kWh of heat energy, and 16kWh of mechanical energy.
Biofuel Ethanol
Being readily available as a waste product with a high content of sugar, and low nutritional value, bagasse has potential as an environmentally friendly alternative to corn as a source of the biofuel ethanol.
Its composition makes it a promising source for second-generation biofuel production. Some studies suggest that it is possible to achieve 149 – 192 liters of ethanol per ton of bagasse.
In some countries, such as Brazil, ethanol produced from the sugar in sugarcane is a very popular fuel.
In addition, the cellulose-rich bagasse is being investigated for its potential for producing commercial quantities of cellulosic ethanol.
Paper Industry
Paper is produced from bagasse in the Middle East, a few Latin American countries, and in sugar-producing countries that are deficient in forest resources.
As we already mentioned, bagasse is also used as a substitute for wood in a number of tropical and subtropical countries for the production of paper, pulp and board, such as Argentina, Thailand, Iran, Colombia, China, and India. It produces pulp with physical properties that are suited for writing papers and generic printing. However, it is also widely used for boxes and newspaper production.
The forest-rich countries are also considering using an agricultural residue in paper production rather than wood since it will add advantages of reducing deforestation. This especially relates to bagasse.
Bagasse Boards
It is considered a good substitute for plywood and can also be used for making boards resembling plywood or particleboard, called Xanita board and Bagasse board.
Bagasse board is also called LDF- Low-Density Fiber Board. It’s especially popular in Bangladesh and India. It’s much cheaper than wood-based boards. It is the main ingredient for the production of pressed building boards as well as other construction materials and can be made into many biodegradable plastics.
Furniture Industry
Additionally, bagasse has wide usage for making, furniture, partitions, etc.
Cattle Feed
Bagasse is used as a source of cellulose for manufacturing animal feeds. By mixing bagasse with enzymes and molasses and fermenting it, K-Much Industry has patented a method of converting it into cattle feed. It is marketed in Australia, Middle East, Taiwan, Korea, Malaysia, Japan, and Thailand as “fiber-rich.”